- $cmd
A virtual collection that exposes MongoDB's database commands. To use database commands, see Issue Commands.一个公开MongoDB数据库命令的虚拟集合。要使用数据库命令,请参阅发布命令。- _id
A field required in every MongoDB document. The _id field must have a unique value.每个MongoDB文档中都需要一个字段。_id字段必须具有唯一值。You can think of the您可以将_idfield as the document's primary key._id字段视为文档的主键。If you create a new document without an如果您创建了一个没有_idfield, MongoDB automatically creates the field and assigns a unique BSON ObjectId to the field._id字段的新文档,MongoDB会自动创建该字段并为该字段分配一个唯一的BSON ObjectId。absolute system CPU utilization绝对系统CPU利用率System CPU utilization relative to the full amount of CPU available to cloud instances that share CPU.系统CPU利用率相对于共享CPU的云实例可用的全部CPU量。When a cloud provider throttles CPU utilization for a cloud instance, the instance's absolute system CPU utilization is equal to the baseline CPU utilization assigned to this instance.当云提供商限制云实例的CPU利用率时,该实例的绝对系统CPU利用率等于分配给该实例的基线CPU利用率。When a cloud provider adds CPU above the baseline CPU, such as through a bursting mechanism, the sum of normalized kernel CPU utilization and user CPU utilization on an instance can exceed the instance's baseline CPU.当云提供商将CPU添加到基线CPU之上时,例如通过突发机制,实例上的归一化内核CPU利用率和用户CPU利用率之和可能会超过实例的基线CPU。In this case, the sum of the normalized kernel CPU utilization and user CPU utilization is still less than the full amount of CPU shared by cloud instances.在这种情况下,标准化的内核CPU利用率和用户CPU利用率之和仍然小于云实例共享的CPU总量。See also relative system CPU utilization, baseline CPU utilization, and burstable instances.另请参阅相对系统CPU利用率、基线CPU利用率和突发实例。
accumulator累加器An expression in an aggregation pipeline that maintains state between documents in the aggregation pipeline.聚合管道中的一个表达式,用于维护聚合管道中文档之间的状态。For a list of accumulator operations, see有关累加器操作的列表,请参阅$group.$group。action操作An operation the user can perform on a resource.用户可以对资源执行的操作。Actions and resources combine to create privileges. See action.操作和资源结合在一起创建权限。见操作。- admin
database数据库 A privileged database. Users must have access to the权限数据库。用户必须有权访问admindatabase to run certain administrative commands. For a list of administrative commands, see Administration Commands.admin数据库才能运行某些管理命令。有关管理命令的列表,请参阅管理命令。Advanced Persistent Threat高级持续性威胁In security, an attacker who gains and maintains long-term access to the network, disk and/or memory and remains undetected for an extended period.在安全领域,攻击者获得并保持对网络、磁盘和/或内存的长期访问,并在很长一段时间内未被发现。aggregation聚合An operation that reduces and summarizes large sets of data. For more information, see Aggregation Operations.一种减少和汇总大量数据的操作。有关更多信息,请参阅聚合操作。aggregation pipeline聚合管道Consists of one or more stages that process documents. Aggregation pipelines offer rich syntax to express complex queries.由处理文档的一个或多个阶段组成。聚合管道提供了丰富的语法来表达复杂的查询。For a list of stages, see Aggregation Stages.有关阶段列表,请参阅聚合阶段。alert警报Notification sent by Atlas when your database operations or server usage reach thresholds that affect cluster performance. To learn what conditions you can set to trigger alerts, see Review Alert Conditions.当数据库操作或服务器使用率达到影响集群性能的阈值时,Atlas会发送通知。要了解可以设置哪些条件来触发警报,请参阅查看警报条件。analytics node分析节点Specialized read-only node that can isolate queries which you do not want to affect your operational workload. Analytics nodes are useful for handling analytic data such as reporting queries executed by BI tools. You can host analytics nodes in dedicated geographic regions to optimize read performance and reduce latency.专门的只读节点,可以隔离您不想影响操作工作负载的查询。分析节点可用于处理分析数据,例如BI工具执行的报告查询。您可以在专用地理区域中托管分析节点,以优化读取性能并减少延迟。- API
Communication protocol facilitating interaction between the client and MongoDB Atlas. You can use the Atlas Administration API to automate many of the tasks performed in the Atlas UI.促进客户端和MongoDB Atlas之间交互的通信协议。您可以使用Atlas Administration API自动执行Atlas UI中执行的许多任务。Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search近似最近邻(ANN)搜索Computational technique used to quickly find points in a dataset that are close to a given query point. Vector Search uses ANN search to find vector embeddings in the data that are closest to the vector embeddings in the query without scanning every vector.用于快速查找数据集中与给定查询点接近的点的计算技术。矢量搜索使用ANN搜索在数据中找到与查询中的矢量嵌入最接近的矢量嵌入,而无需扫描每个矢量。arbiter仲裁器A replica set member that exists just to vote in elections. Arbiters do not replicate data. An arbiter participates in elections for a primary but cannot become a primary. For more details, see Replica Set Arbiter.仅为在选举中投票而存在的副本集成员。仲裁员不复制数据。仲裁者参与primary,但不能成为primary。有关更多详细信息,请参阅副本集仲裁器。- Atlas
- MongoDB Atlas
is a cloud-hosted database-as-a-service.是一种云托管的数据库即服务。 - Atlas
user用户 Account used to access the MongoDB Atlas application. You can grant MongoDB Atlas users access to MongoDB Atlas organizations, projects, or both, with certain permissions defined by user roles.用于访问MongoDB Atlas应用程序的帐户。您可以授予MongoDB Atlas用户访问MongoDB Atlas组织、项目或两者的权限,这些权限由用户角色定义。A MongoDB Atlas user is different than a database user. MongoDB Atlas users do not provide access to any MongoDB databases.MongoDB Atlas用户与数据库用户不同。MongoDB Atlas用户不提供对任何MongoDB数据库的访问。- Atlas
user role用户角色 Set of permissions granted to an Atlas user.授予Atlas用户的权限集。You can grant permissions at the organization or project level.您可以在组织或项目级别授予权限。atomic operation原子操作An atomic operation is a write operation that either completes entirely or doesn't complete at all.原子操作是一种写操作,它要么完全完成,要么根本不完成。For distributed transactions, which involve writes to multiple documents, all writes to each document must succeed for the transaction to succeed.对于涉及写入多个文档的分布式事务,对每个文档的所有写入都必须成功,事务才能成功。Atomic operations cannot partially complete. See Atomicity and Transactions.原子操作不能部分完成。参见原子性和事务。authentication认证Verification of the user identity. See Authentication on Self-Managed Deployments.用户身份验证。请参阅自我管理部署上的身份验证。authorization授权Provisioning of access to databases and operations. See Role-Based Access Control in Self-Managed Deployments.提供对数据库和操作的访问。请参阅自我管理部署中的基于角色的访问控制。auto-scaling自动缩放Configurable option to have your cluster automatically increase or decrease its cluster tier, storage capacity, or both in response to cluster usage.可配置选项,使集群根据集群使用情况自动增加或减少其集群层、存储容量或两者兼而有之。automatic encryption自动加密When using In-Use Encryption, automatically performing encryption and decryption based on your preconfigured encryption schema.使用使用中加密时,根据预配置的加密模式自动执行加密和解密。The Automatic Encryption Shared Library translates MongoDB Query Language into the correct call, meaning you don't need to rewrite your application for specific encrypt and decrypt calls.自动加密共享库将MongoDB查询语言转换为正确的调用,这意味着您不需要为特定的加密和解密调用重写应用程序。- B-tree
A data structure commonly used by database management systems to store indexes. MongoDB uses B-tree indexes.数据库管理系统通常用于存储索引的数据结构。MongoDB使用B树索引。- backup
Copy of your data that encapsulates the state of your cluster at a given time. Backups provide a safety measure in the case of data loss events.封装给定时间集群状态的数据副本。备份在发生数据丢失事件时提供了一种安全措施。MongoDB Atlas provides fully-managed Cloud Backups.MongoDB Atlas提供完全托管的云备份。backup cursor备份游标A tailable cursor that points to a list of backup files. Backup cursors are for internal use only.指向备份文件列表的可尾随游标。备份游标仅供内部使用。balancer平衡器An internal MongoDB process that runs in the context of a sharded cluster and manages the migration of chunks. Administrators must disable the balancer for all maintenance operations on a sharded cluster.一个在分片集群环境中运行并管理块迁移的内部MongoDB进程。管理员必须对分片群集上的所有维护操作禁用平衡器。See Sharded Cluster Balancer.请参阅分片集群平衡器。baseline CPU utilization基准CPU利用率Fraction of the full amount of CPU available to cloud instances that share CPU. A cloud provider assigns a certain amount of baseline CPU to each cloud instance, based on the instance's cluster tier.共享CPU的云实例可用CPU总量的一部分。云提供商根据实例的集群层为每个云实例分配一定数量的基线CPU。Typically, baseline CPU utilization falls between 20% and 50% of absolute system CPU utilization.通常,基线CPU利用率在绝对系统CPU利用率的20%到50%之间。See also relative system CPU utilization and burstable instances.另请参见相对系统CPU利用率和突发实例。- big-endian
A byte order in which the most significant byte (big end) of a multibyte data value is stored at the lowest memory address.一种字节顺序,其中多字节数据值的最高有效字节(大端)存储在最低内存地址。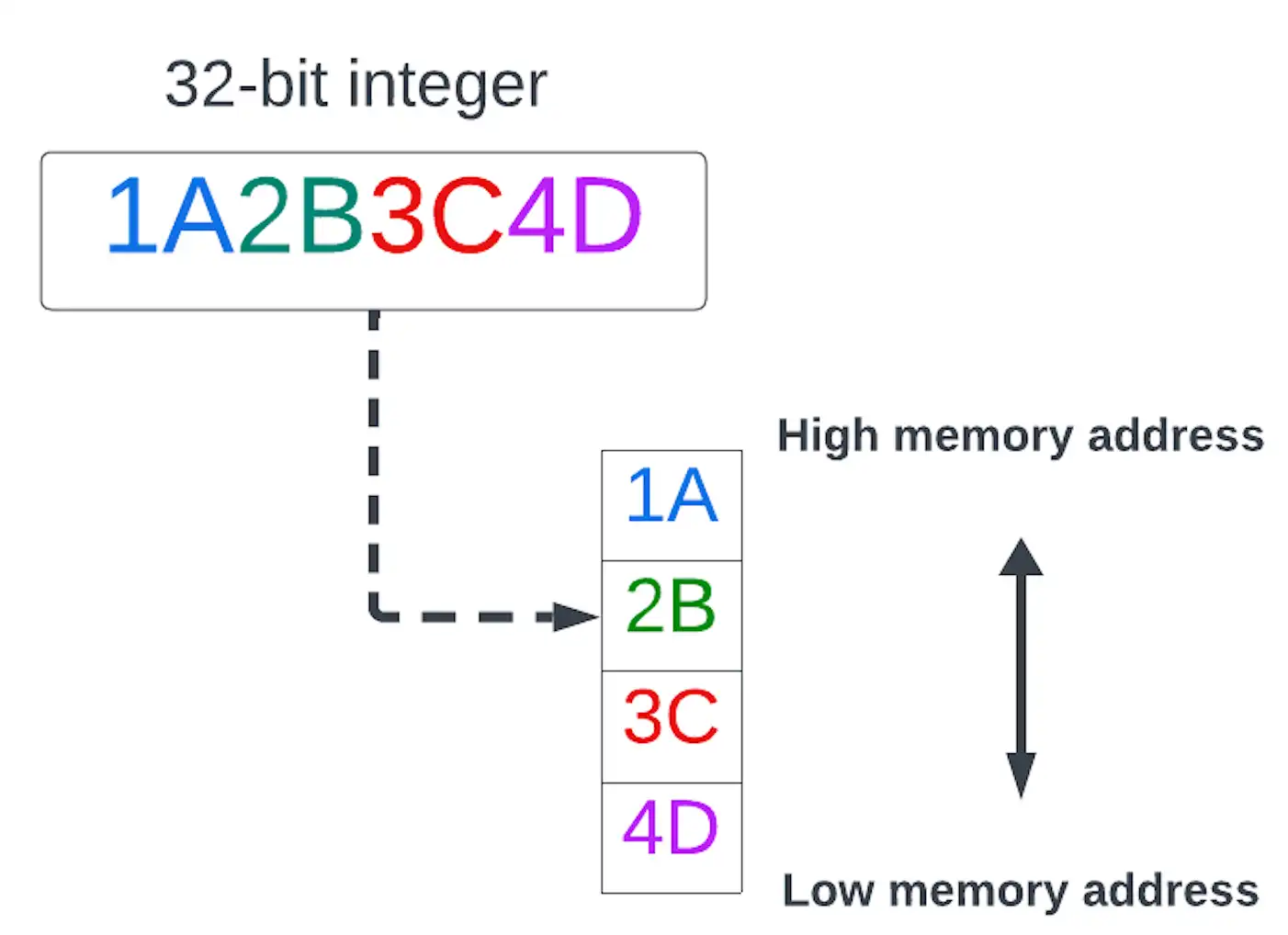
blocking sort阻塞排序A sort that must be performed in memory before the output is returned. In-memory sorts may impact performance for large data sets. Use an indexed sort to avoid an in-memory sort.在返回输出之前必须在内存中执行的排序。内存排序可能会影响大型数据集的性能。使用索引排序以避免内存中的排序。bounded collection scan有界集合扫描A plan used by the query optimizer that excludes documents with specific field value ranges.查询优化器使用的一种计划,排除具有特定字段值范围的文档。For example, if a range of date field values is outside of a specified date range, the documents in that range are excluded from the query plan.例如,如果日期字段值的范围在指定的日期范围之外,则该范围内的文档将被排除在查询计划之外。See Collection Scan.请参阅集合扫描。- BSON
A serialization format used to store documents and make remote procedure calls in MongoDB. "BSON" is a combination of the words "binary" and "JSON". Think of BSON as a binary representation of JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) documents.一种序列化格式,用于在MongoDB中存储文档和进行远程过程调用。“BSON”是单词“binary”和“JSON”的组合。将BSON视为JSON(JavaScript对象表示法)文档的二进制表示。See BSON Types and MongoDB Extended JSON (v2).请参阅BSON类型和MongoDB扩展JSON(v2)。- BSON types
The set of types supported by the BSON serialization format.BSON序列化格式支持的类型集。For a list of BSON types, see BSON Types.有关BSON类型的列表,请参阅BSON类型。burstable instances突发实例Cloud instance types that share a common physical CPU that, for some cloud providers, use a "CPU credit" model. When you use burstable instances, portions of shared CPU may either become available to each of the virtual instances or may become unavailable, under different demands on the instance resources.共享公共物理CPU的云实例类型,对于某些云提供商来说,使用“CPU信用”模型。当您使用突发实例时,在对实例资源的不同需求下,共享CPU的部分可能会对每个虚拟实例可用,也可能不可用。To learn more, see AWS burstable instances, Azure disk bursting, and GCP CPU Bursting. See also baseline CPU utilization, absolute system CPU utilization, and relative system CPU utilization.要了解更多信息,请参阅AWS突发实例、Azure磁盘突发和GCP CPU突发。另请参阅基准CPU利用率、绝对系统CPU利用率和相对系统CPU利用度。CAP theoremCAP定理Given three properties of computing systems, consistency, availability, and partition tolerance, a distributed computing system can provide any two of these features, but never all three.给定计算系统的三个属性,一致性、可用性和分区容忍度,分布式计算系统可以提供其中任何两个特性,但永远不能提供所有三个特性。capped collection固定集合A fixed-sized collection that automatically overwrites its oldest entries when the collection reaches its maximum size.一个固定大小的集合,当集合达到其最大大小时,会自动覆盖其最旧的条目。The MongoDB oplog that is used in replication is a capped collection. See Capped Collections.用于复制的MongoDB oplog是一个有上限的集合。请参阅封顶集合。cardinality基数The measure of the number of elements within a set of values. For example, the set一组值中元素数量的度量。例如,集合A = { 2, 4, 6 }contains 3 elements, and has a cardinality of 3.A={2,4,6}包含3个元素,基数为3。See Shard Key Cardinality.请参阅分片键基数。cartesian product笛卡尔积The result of combining two data sets where the combined set contains every possible combination of values.组合两个数据集的结果,其中组合集包含所有可能的值组合。- cfq
Complete Fairness Queueing (cfq) is an I/O operation scheduler that allocates bandwidth for incoming request processes.完全公平排队(cfq)是一种为传入请求进程分配带宽的I/O操作调度器。- checksum
A calculated value used to ensure data integrity. The md5 algorithm is sometimes used as a checksum.用于确保数据完整性的计算值。md5算法有时被用作校验和。- chunk
A contiguous range of shard key values within a shard. Chunk ranges are inclusive of the lower boundary and exclusive of the upper boundary.分片内连续的分片键值范围。块状范围包括下边界,不包括上边界。MongoDB splits chunks when they grow bigger than the configured chunk size. The default chunk size is 128 megabytes. MongoDB migrates chunks when a shard contains too many chunks of a collection relative to other shards.当块的大小超过配置的块大小时,MongoDB会对块进行拆分。默认块大小为128 MB。当一个分片包含的集合块相对于其他分片太多时,MongoDB会迁移块。For more details, see Data Partitioning with Chunks, Sharded Cluster Balancer, and Manage Sharded Cluster Balancer.有关更多详细信息,请参阅使用块的数据分区、分片集群平衡器和管理分片集群均衡器。client客户端The application layer that uses a database for data persistence and storage. Drivers provide the interface level between the application layer and the database server.使用数据库进行数据持久性和存储的应用层。驱动程序提供应用层和数据库服务器之间的接口级别。A client can also be a single thread or process.客户端也可以是单个线程或进程。client affinity客户端关联A consistent client connection to a specified data source.与指定数据源的一致客户端连接。cloud backups云备份Localized cluster backup storage using the native snapshot functionality of the cluster's cloud service provider.使用集群云服务提供商的本机快照功能进行本地化集群备份存储。MongoDB Atlas supports Cloud Backups for clusters served on:MongoDB Atlas支持以下集群的云备份:cluster群集Set of nodes comprising a MongoDB deployment. Clusters can be replica sets or sharded deployments.组成MongoDB部署的一组节点。集群可以是副本集或分片部署。cluster class集群类Configurable for M40+ clusters hosted on AWS.可配置为托管在AWS上的M40+集群。Storage class of your cluster. Your selected class affects cluster storage performance and cluster costs. You can choose one of the following classes:集群的存储类。您选择的类会影响群集存储性能和群集成本。您可以选择以下课程之一:Low CPU低CPUGeneral通用Local NVMe SSD本地NVMe SSD
cluster tier集群层Dictates the memory, storage, vCPUs, and IOPS specification for each data-bearing server in the cluster. Cluster storage size and overall performance increase as the cluster tier increases.规定集群中每个数据承载服务器的内存、存储、vCPU和IOPS规范。群集存储大小和整体性能随着群集层的增加而增加。cluster-to-cluster sync集群间同步Synchronizes data between sharded clusters. Also known as C2C sync.在分片集群之间同步数据。也称为C2C同步。clustered collection集群集合A collection that stores documents ordered by a clustered index key.按聚集索引键顺序存储文档的集合。See Clustered Collections.请参见群集集合。- CMK
Abbreviation of Customer Master Key, see Customer Master Key.客户主键的缩写,请参阅客户主键。collection集合A grouping of MongoDB documents. A collection is the equivalent of an RDBMS table. A collection is in a single database. Collections do not enforce a schema. Documents in a collection can have different fields. Typically, documents in a collection have a similar or related purpose.一组MongoDB文档。集合相当于RDBMS表。集合位于单个数据库中。集合不强制执行架构。集合中的文档可以有不同的字段。通常,集合中的文档具有相似或相关的目的。See Namespaces.请参见命名空间。collection scan集合扫描Collection scans are a query execution strategy where MongoDB must inspect every document in a collection to see if it matches the query criteria. These queries are very inefficient and don't use indexes.集合扫描是一种查询执行策略,MongoDB必须检查集合中的每个文档,看看它是否符合查询条件。这些查询非常低效,不使用索引。See Query Optimization for details about query execution strategies.有关查询执行策略的详细信息,请参阅查询优化。commit提交Saves data changes made after the start of the保存启动startSessioncommand.startSession命令后所做的数据更改。Operations within a transaction are not permanent until they are committed with the事务中的操作在使用commitTransactioncommand.commitTransaction命令提交之前不是永久性的。commit quorum提交仲裁During an index build the commit quorum specifies how many secondaries must be ready to commit their local index build before the primary node performs the commit.在索引构建过程中,提交仲裁指定了在主节点执行提交之前,必须有多少辅助节点准备好提交其本地索引构建。compound index复合索引An index consisting of two or more keys. See Compound Indexes.由两个或多个键组成的索引。请参见复合指数。concurrency control并发控制Concurrency control ensures that database operations can be executed concurrently without compromising correctness.并发控制确保数据库操作可以并发执行,而不会影响正确性。Pessimistic concurrency control, such as that used in systems with locks, blocks any potentially conflicting operations even if they may not conflict.悲观并发控制,例如在有锁的系统中使用的并发控制,会阻止任何潜在的冲突操作,即使它们可能没有冲突。Optimistic concurrency control, the approach used by WiredTiger, delays checking until after a conflict may have occurred, ending and retrying one of the operations in any write conflict.WiredTiger使用的乐观并发控制方法将检查延迟到可能发生冲突之后,在任何写入冲突中结束并重试其中一个操作。config database配置数据库An internal database with metadata for a sharded cluster. Typically, you don't modify the一个包含分片集群元数据的内部数据库。通常,您不会修改configdatabase. For more information about theconfigdatabase, see Config Database.config数据库。有关config数据库的更多信息,请参阅config数据库。config server配置服务器A存储与分片集群关联的所有元数据的mongodinstance that stores all the metadata associated with a sharded cluster. See Config Servers.mongod实例。请参阅配置服务器。config shard配置分片A一个mongodinstance that stores all the metadata associated with a sharded cluster and can also store application data.mongod实例,存储与分片集群相关的所有元数据,也可以存储应用程序数据。See Config Shards.请参阅配置分片。connection pool连接池A cache of database connections maintained by the driver. The cached connections are re-used when connections to the database are required, instead of opening new connections.由驱动程序维护的数据库连接缓存。当需要连接到数据库时,缓存的连接会被重新使用,而不是打开新的连接。connection storm连接风暴A scenario where a driver attempts to open more connections to a deployment than that deployment can handle. When requests for new connections fail, the driver requests to establish even more connections in response to the deployment slowing down or failing to open new connections. These continuous requests can overload the deployment and lead to outages.驱动程序试图打开的与部署的连接数超过该部署所能处理的连接数的情况。当新连接的请求失败时,驱动程序会请求建立更多的连接,以响应部署速度减慢或无法打开新连接。这些持续的请求可能会使部署过载并导致中断。container容器A collected set of software and its dependent libraries that are packaged together to make transferring between computing environments easier. Containers run as compartmentalized processes on your operating system, and can be given their own resource constraints. Common container technologies are Docker and Kubernetes.一组集合的软件及其依赖库打包在一起,使计算环境之间的传输更容易。容器在操作系统上作为划分的进程运行,并且可以被赋予自己的资源约束。常见的容器技术是Docker和Kubernetes。contention factor争用因素Multiple operations attempting to modify the same resource, such as a document field, cause conflicts that delay operations. The contention factor is a setting used with Queryable Encryption to internally partition encrypted field/value pairs and optimize operations.试图修改同一资源(如文档字段)的多个操作会导致冲突,从而延迟操作。争用因子是与可查询加密一起使用的设置,用于在内部对加密的字段/值对进行分区并优化操作。See contention.请参阅争论。cosine similarity余弦相似度Metric that uses the angle between two vectors to determine the similarity between those vectors. Cosine similarity is sensitive to vector orientation. You can use cosine similarity function when indexing your vector embeddings for Vector Search.使用两个向量之间的角度来确定这些向量之间相似性的度量。余弦相似度对矢量方向很敏感。在为矢量搜索的矢量嵌入建立索引时,可以使用余弦相似性函数。If the vectors are normalized to unit length, use dotProduct similarity function instead.如果向量被归一化为单位长度,则使用dotProduct相似性函数。CPU stealCPU被盗The percentage by which the CPU usage exceeds the guaranteed baseline CPU credit accumulation rate. CPU steal is relevant for cloud providers that rely on the credit model in their bursting strategy. CPU credits are units of CPU utilization that you accumulate.CPU使用率超过保证的基准CPU信用累积率的百分比。CPU窃取与依赖信用模型的云提供商的爆发策略有关。CPU积分是您累积的CPU利用率单位。The credits accumulate at a constant rate to provide a guaranteed level of performance. You can use these credits for additional CPU performance. When the credit balance is exhausted, MongoDB only provides the guaranteed baseline of CPU performance and displays the amount of excess as steal percent See also relative system CPU utilization, baseline CPU utilization, and burstable instances.学分以恒定的速率累积,以提供有保证的性能水平。您可以使用这些积分来获得额外的CPU性能。当信用余额用尽时,MongoDB只提供CPU性能的保证基线,并将超额金额显示为窃取百分比。另请参阅a href="#std-term-relative-system-CPU-utilization">相对系统CPU利用率、基线CPU利用率和突发实例。- CRUD
An acronym for the fundamental operations of a database: Create, Read, Update, and Delete. See MongoDB CRUD Operations.数据库基本操作的缩写:创建、读取、更新和删除。请参阅MongoDB CRUD操作。- CSV
A text data format with comma-separated values. CSV files can be used to exchange data between relational databases because CSV files have tabular data.一种以逗号分隔的文本数据格式。CSV文件可用于在关系数据库之间交换数据,因为CSV文件具有表格数据。You can import CSV files using您可以使用mongoimport.mongoimport导入CSV文件。cursor游标A pointer to the result set of a query. Clients can iterate through a cursor to retrieve results. By default, cursors not opened within a session automatically timeout after 10 minutes of inactivity. Cursors opened in a session close with the end or timeout of the session.指向查询结果集的游标。客户端可以遍历游标以检索结果。默认情况下,会话中未打开的游标在10分钟不活动后会自动超时。在会话结束或超时时关闭的会话中打开的游标。See Cursors.请参阅游标。custom role自定义角色Custom set of MongoDB privilege actions and MongoDB roles that you can save and assign to a database user.您可以保存并分配给数据库用户的自定义MongoDB权限操作和MongoDB角色集。Create custom roles when MongoDB Atlas's built-in roles don't describe your desired set of privileges.当MongoDB Atlas的内置角色无法描述您所需的权限集时,创建自定义角色。Customer Master Key客户主键A key that encrypts your Data Encryption Key. The customer master key must be hosted in a remote key provider.对数据加密键进行加密的键。客户主键必须托管在远程键提供程序中。daemon守护进程A background, non-interactive process.一个背景的、非互动的过程。data directory数据目录The file system location wheremongodstores data files.dbPathspecifies the data directory.mongod存储数据文件的文件系统位置。dbPath指定数据目录。Data Encryption Key数据加密键A key you use to encrypt the fields in your MongoDB documents. The encrypted Data Encryption Key is stored in your Key Vault collection.用于加密MongoDB文档中字段的键。加密的数据加密键存储在键库集合中。The Data Encryption Key is encrypted by the Customer Master Key.数据加密键由客户主键加密。Data Explorer数据浏览器Tool within MongoDB Atlas to view and interact with cluster data. You can also use the Data Explorer to manage indexes and run aggregation pipelines to process your data.MongoDB Atlas中的工具,用于查看集群数据并与之交互。您还可以使用数据资源管理器来管理索引并运行聚合管道来处理数据。Data Federation数据联合MongoDB's solution for querying data stored in low-cost S3 buckets, MongoDB Atlas clusters, and HTTP endpoints using the MongoDB Query Language. Analytics applications can use Atlas Data Federation to make use of archived data for their data processing needs.MongoDB使用MongoDB查询语言查询存储在低成本S3桶、MongoDB Atlas集群和HTTP端点中的数据的解决方案。分析应用程序可以使用Atlas Data Federation来利用存档数据满足其数据处理需求。data files数据文件Store document data and indexes. The存储文档数据和索引。dbPathoption specifies the file system location for the data files.dbPath选项指定数据文件的文件系统位置。data ingestion pipeline数据摄取管道Workflow for organizing and transforming data by using RAG and storing it in a vector database such as MongoDB Atlas.使用RAG组织和转换数据并将其存储在MongoDB Atlas等矢量数据库中的工作流程。data partition数据分区A distributed system architecture that splits data into ranges. Sharding uses partitioning.一种将数据划分为不同范围的分布式系统架构。分片使用分区。See Data Partitioning with Chunks.请参阅使用块进行数据分区。data-center awareness数据中心意识A property that allows clients to address members in a system based on their locations.一种属性,允许客户端根据成员的位置对系统中的成员进行寻址。Replica sets implement data-center awareness using tagging. See Data Center Awareness.副本集使用标记实现数据中心感知。请参阅数据中心意识。database数据库A container for collections. Each database has a set of files in the file system. One MongoDB server typically has multiple databases.集合的容器。每个数据库在文件系统中都有一组文件。一个MongoDB服务器通常有多个数据库。database command数据库命令A MongoDB operation, other than an insert, update, remove, or query. For a list of database commands, see Database Commands. To use database commands, see Issue Commands.MongoDB操作,而不是插入、更新、删除或查询。有关数据库命令的列表,请参阅数据库命令。要使用数据库命令,请参见发布命令。database exfiltration数据库泄漏Database exfiltration refers to an authorized party taking data from a secured system and either sharing it with an unauthorized party or storing it on an unsecured system. This may be malicious or accidental.数据库泄露是指授权方从安全系统中获取数据,并与未经授权方共享或将其存储在不安全的系统中。这可能是恶意的或意外的。database profiler数据库分析器A tool that, when enabled, keeps a record on all long-running operations in a database's一种工具,启用后,会在数据库的system.profilecollection.system.profile集合中记录所有长时间运行的操作。The profiler is most often used to diagnose slow queries.分析器最常用于诊断慢速查询。See Database Profiler.请参阅数据库分析器。database user数据库用户Credentials used to authenticate a client to access a MongoDB cluster.用于验证客户端访问MongoDB集群的凭据。You can assign privileges to a database user to determine that user's access level to a cluster.您可以为数据库用户分配权限,以确定该用户对集群的访问级别。Database users are different from Atlas users. Database users have access to MongoDB deployments, not the MongoDB Atlas application.数据库用户与Atlas用户不同。数据库用户可以访问MongoDB部署,而不是MongoDB Atlas应用程序。- dbpath
The location of MongoDB's data file storage. SeeMongoDB数据文件存储的位置。请参见dbPath.dbPath。- DDL
(Data Definition Language)(数据定义语言) DDL includes commands that create and modify collections and indexes.DDL包括创建和修改集合和索引的命令。dead letter queue死信队列A dead letter queue is a collection within an MongoDB Atlas database that stores documents that throw errors during ingestion.死信队列是MongoDB Atlas数据库中的一个集合,用于存储在摄取过程中抛出错误的文档。dedicated cluster专用机群Cluster category containing clusters of tier集群类别包含M10and greater.M10及以上级别的集群。Tier等级Recommended environments推荐环境M10andM20Development开发Low-traffic production低流量生产
M30and greaterProduction生产dedicated config server专用配置服务器A一个mongodinstance that only stores all the metadata associated with a sharded cluster.mongod实例,只存储与分片集群相关的所有元数据。- DEK
Data Encryption Key. For more details, see Data Encryption Key.数据加密键。有关更多详细信息,请参阅数据加密键。delayed member延迟成员A replica set member that cannot become primary and applies operations at a specified delay. The delay is useful for protecting data from human error (unintentionally deleted databases) or updates that have unforeseen effects on the production database.无法成为主副本集成员并在指定延迟后应用操作的副本集成员。延迟对于保护数据免受人为错误(无意删除的数据库)或对生产数据库产生不可预见影响的更新非常有用。See Delayed Replica Set Members.请参见延迟副本集成员。dense vectors密集向量Numeric representation of data where most or all of the dimensions contain non-zero values. Vector Search uses dense vectors, which are packed with more data, to capture more complex relationships.数据的数值表示,其中大多数或所有维度包含非零值。矢量搜索使用包含更多数据的密集矢量来捕获更复杂的关系。deployment部署A group of MongoDB servers containing your data. MongoDB Atlas-managed clusters are clusters (replica sets or sharded clusters).一组包含您数据的MongoDB服务器。MongoDB Atlas管理的集群是集群(副本集或分片集群)。dimensions维度Number of components or elements that make up the features or attributes of data in multi-dimensional space. Vector Search supports up to构成多维空间中数据特征或属性的组件或元素的数量。矢量搜索在索引和查询时最多支持4096dimensions at index-time and query-time.4096个维度。document文件A record in a MongoDB collection and the basic unit of data in MongoDB. Documents are analogous to JSON objects but exist in the database in a more type-rich format known as BSON.MongoDB集合中的记录和MongoDB中的基本数据单位。文档类似于JSON对象,但以一种更富类型的格式存在于数据库中,称为BSON。See Documents.请参阅文档。- dot notation
MongoDB uses the dot notation to access the elements of an array and to access the fields of an embedded document.MongoDB使用点符号来访问数组的元素和嵌入式文档的字段。See Dot Notation.请参阅点符号。dotProduct similarity点积相似性Measures similarity between two vectors in multi-dimensional space and returns a scalar value, which is positive when the vectors point in roughly the same direction, negative when the vectors point in opposite direction, and zero when the vectors have no similarity.度量多维空间中两个向量之间的相似性,并返回一个标量值,当向量指向大致相同的方向时,该标量值为正,当向量朝向相反的方向时为负,当向量没有相似性时为零。Vector Search supports using矢量搜索支持在搜索最近邻时使用dotproductsimilarity function when searching for nearest neighbors. We recommend this similarity function instead of cosine similarity if the vectors are normalized to unit length.dotproduct相似性函数。如果向量被归一化为单位长度,我们建议使用这种相似性函数而不是余弦相似性。draining耗尽- The process of removing or "shedding" chunks from one shard to another. Administrators must drain shards before removing them from the cluster. See Remove Shards from a Sharded Cluster.
driver驱动程序A client library for interacting with MongoDB in a particular computer language. See driver.用于以特定计算机语言与MongoDB交互的客户端库。见驱动程序。durable耐用的A write operation is durable when it persists after a shutdown (or crash) and restart of one or more server processes.当一个或多个服务器进程关闭(或崩溃)并重新启动后,写入操作仍然存在时,写入操作是持久的。For a single对于单个mongodserver, a write operation is considered durable when it has been written to the server's journal file.mongod服务器,当写入操作被写入服务器的日志文件时,它被认为是持久的。For a replica set, a write operation is considered durable after the write operation achieves durability on a majority of voting nodes and written to a majority of voting nodes' journals.对于副本集,在写入操作在大多数投票节点上达到持久性并写入大多数投票节点的日志后,写入操作被认为是持久的。electable node可选举节点- Node which is eligible to become the primary member of your replica set. MongoDB Atlas prioritizes nodes in the highest priority region for primary eligibility during elections. To ensure reliable elections, the total number of electable nodes across an entire region must be 3, 5, or 7.
election选举- The process where members of a replica set select a primary on startup and in the event of a failure. See Replica Set Elections.
embedding嵌入Representation of data such as text, images, audio, video, and so on as an array of numbers, which can be interpreted as coordinates in multi-dimensional space. MongoDB Atlas supports storing embeddings in an MongoDB Atlas cluster and Vector Search supports indexing and querying vector embeddings of up to将文本、图像、音频、视频等数据表示为数字数组,可以将其解释为多维空间中的坐标。MongoDB Atlas支持在MongoDB Atlas集群中存储嵌入,Vector Search支持索引和查询高达4096dimensions.4096维的向量嵌入。encryption key加密键Random string of bits generated specifically to encrypt and decrypt data.为加密和解密数据而专门生成的随机比特串。MongoDB Atlas
Project Ownerscan configure an additional layer of encryption on their data in addition to the default encryption at rest that MongoDB Atlas provides. Project owners can use their MongoDB Atlas-compatible customer key management provider with the MongoDB encrypted storage engine.MongoDB Atlas supports the following customer key management providers when configuring Encryption at Rest:配置静态加密时,MongoDB Atlas支持以下客户键管理提供程序:encryption schema加密模式- In Queryable Encryption, the encryptedFields document that defines which fields are queryable and which query types are permitted on those fields.
endianness字节序In computing, endianness refers to the order in which bytes are arranged. This ordering can refer to transmission over a communication medium or more commonly how the bytes are ordered in computer memory, based on their significance and position.在计算中,字节序是指字节的排列顺序。这种排序可以指通过通信介质的传输,或者更常见的是指如何根据字节的重要性和位置在计算机内存中对字节进行排序。For details, see big-endian and little-endian.有关详细信息,请参阅大端序和小端序。- envelope encryption
- An encryption procedure where data is encrypted using a Data Encryption Key and the data encryption key is encrypted by another key called the Customer Master Key. The encrypted keys are stored as BSON documents in a MongoDB collection called the KeyVault.
euclidean similarity欧几里德相似性- Formula to calculate the similarity by using the distance between two vectors in multi-dimensional space. Euclidean distance is sensitive to the magnitude of the vectors. Vector Search supports using
euclideansimilarity function for indexing vectors and when searching for nearest neighbors. eventual consistency最终一致性A property of a distributed system that allows changes to the system to propagate gradually. In a database system, this means that readable members aren't required to have the latest updates.分布式系统的一种属性,允许对系统的更改逐渐传播。在数据库系统中,这意味着可读成员不需要拥有最新更新。explicit encryption显式加密- When using In-Use Encryption, explicitly specifying the encryption or decryption operation, keyID, and query type (for Queryable Encryption) or algorithm (for Client-Side Field Level Encryption) when working with encrypted data. Compare to automatic encryption.
expression表达A component of a query that resolves to a value. Expressions are stateless, meaning they return a value without mutating any of the values used to build the expression.查询中解析为值的组件。表达式是无状态的,这意味着它们返回的值不会改变用于构建表达式的任何值。In the MongoDB Query Language, you can build expressions from the following components:在MongoDB查询语言中,您可以从以下组件构建表达式:Component Example示例Constants常量3Operators运算符$addField path expressions字段路径表达式"$<path.to.field>"For example,
{ $add: [ 3, "$inventory.total" ] }is an expression that consists of the$addoperator and two operands:- The constant
3 - The field path expression
"$inventory.total"
The expression returns the result of adding 3 to the value at path
inventory.totalof the input document.- The constant
- failover
- The process that allows a secondary member of a replica set to become primary in the event of a failure. See Automatic Failover.
field字段- A name-value pair in a document. A document has zero or more fields. Fields are analogous to columns in relational databases. See Document Structure.
- field path
Path to a field in a document. To specify a field path, use a string that prefixes the field name with a dollar sign (文档中字段的路径。要指定字段路径,请使用一个字符串,在字段名称前加上美元符号($).$)。firewall防火墙A system level network filter that restricts access based on IP addresses and other parameters. Firewalls are part of a secure network. See Firewalls.一种系统级网络筛选器,根据IP地址和其他参数限制访问。防火墙是安全网络的一部分。请参阅防火墙。- free tier
Free-to-use cluster tier that provides a small-scale development environment to host your data.免费使用的集群层,提供了一个小规模的开发环境来托管数据。Free clusters never expire, and provide access to a subset of Atlas features and functionality. Free clusters might also be referred to by their instance size,免费集群永不过期,并提供对Atlas特性和功能子集的访问。自由集群也可以通过其实例大小M0.M0来指代。- fsync
A system call that flushes all dirty, in-memory pages to storage. As applications write data, MongoDB records the data in the storage layer.将所有脏的内存页刷新到存储器的系统调用。当应用程序写入数据时,MongoDB会将数据记录在存储层中。To provide durable data, WiredTiger uses checkpoints. For more details, see Journaling and the WiredTiger Storage Engine.
- geohash
A geohash value is a binary representation of the location on a coordinate grid.地理哈希值是坐标网格上位置的二进制表示。See Geohash Values.请参见Geohash值。- GeoJSON
- A geospatial data interchange format based on JavaScript Object Notation (JSON). GeoJSON is used in geospatial queries. For supported GeoJSON objects, see Geospatial Data. For the GeoJSON format specification, see https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7946#section-3.1.
geospatial地理空间Relating to geographical location. See Geospatial Queries.与地理位置有关。请参见地理空间查询。global cluster全球集群Clusters with defined geographic zones to support location-aware read and write operations for globally distributed application instances and clients. You can enable global sharding on clusters of tier具有定义的地理区域的集群,以支持全球分布式应用程序实例和客户端的位置感知读写操作。您可以在M30and greater.M30及更高级别的集群上启用全局分片。- global write zone
Geographic zone representing a subset of your global cluster distribution. Each global cluster supports up to 9 distinct global write zones. Each zone consists of one highest priority region and one or more electable, read-only, or analytics regions.
The available geographic regions depend on the selected cloud service provider.
- GridFS
- A convention for storing large files in a MongoDB database. All of the official MongoDB drivers support the GridFS convention, as does the
mongofilesprogram. See GridFS for Self-Managed Deployments. - group
- See project.
- group ID
- See project ID.
hashed shard key哈希分片键- A type of shard key that uses a hash of the value in the shard key field to distribute documents among members of the sharded cluster. See Hashed Indexes.
- health manager
- A health manager runs health checks on a health manager facet at a specified intensity level. The health manager checks are run at specified time intervals. A health manager can be configured to move a failing mongos out of a cluster automatically.
health manager facet健康经理方面- A set of features that a health manager can be configured to run health checks for. For example, you can configure a health manager to monitor and manage DNS or LDAP cluster health issues automatically. See Health Manager Facets for details.
- hidden member
- A replica set member that cannot become primary and are invisible to client applications. See Hidden Replica Set Members.
- hierarchical navigable small worlds graphs
- Algorithm for performing efficient nearest neighbor search in multi-dimensional space. Vector Search performs ANN search with Hierarchical Navigable Small Worlds.
- high availability
High availability indicates a system designed for durability, redundancy, and automatic failover. Applications supported by the system can operate without downtime for a long time period. MongoDB replica sets support high availability when deployed according to the best practices.
For guidance on replica set deployment architecture, see Replica Set Deployment Architectures.
- highest priority region
Region in a multi-region cluster which MongoDB Atlas prioritizes for primary eligibility during elections.
- hybrid search
- Method of combining different search methods, such as a full-text and a semantic search, to take advantage of their respective strengths. The results are combined by using a technique such as Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF).
- idempotent
- An operation produces the same result with the same input when run multiple times.
- impact
Estimated performance improvement of an index that Performance Advisor suggests.
- in-memory sort
A sort that must be performed in memory before the output is returned. In-memory sorts may impact performance for large data sets. Use an indexed sort to avoid an in-memory sort.
See Sort and Index Use for more information on indexed sort operations.
- In-Use Encryption
- Encryption that secures data when transmitted, stored, and processed, and enables supported queries on that encrypted data. MongoDB provides two approaches to In-Use Encryption: Queryable Encryption and Client-Side Field Level Encryption.
- index
- A data structure that optimizes queries. See Indexes.
- index bounds
- The range of index values that MongoDB searches when using an index to run a query. To learn more, see Multikey Index Bounds.
- indexed sort
- A sort where an index provides the sorted result. Sort operations that use an index often have better performance than an in-memory sort. See Use Indexed to Sort Query Results for more information.
- init script
- A shell script used by a Linux platform's init system to start, restart, or stop a daemon process. If you installed MongoDB using a package manager, an init script is provided for your system as part of the installation. See the respective Installation Guide for your operating system.
- init system
- The init system is the first process started on a Linux platform after the kernel starts, and manages all other processes on the system. The init system uses an init script to start, restart, or stop a daemon process, such as
mongodormongos. Recent Linux versions typically use the systemd init system and thesystemctlcommand. Older Linux versions typically use the System V init system and theservicecommand. See the Installation Guide for your operating system. - initial sync
- The replica set operation that replicates data from an existing replica set member to a new replica set member. See Initial Sync.
- intent lock
- A lock on a resource that indicates the lock holder will read from (intent shared) or write to (intent exclusive) the resource using concurrency control at a finer granularity than that of the resource with the intent lock. Intent locks allow concurrent readers and writers of a resource. See What type of locking does MongoDB use?.
- interface endpoint
AWS VPC endpoint with a private IP address that sends traffic to the MongoDB Atlas private endpoint service over AWS PrivateLink.
- interrupt point
- A point in an operation when it can safely end. MongoDB only ends an operation at designated interrupt points. See Terminate Running Operations.
- IP access list
List of IP addresses and CIDR blocks with access to clusters within an MongoDB Atlas project. For client connections over the public Internet, MongoDB Atlas allows connections to a cluster only from entries in the corresponding project's IP access list. The access list may have up to 200 entries.
MongoDB Atlas also allows client connections over nonpublic networking, such network peering connections or private endpoints. These types of connections work irrespective of the IP access list. To learn more, see Set Up a Network Peering Connection and Learn About Private Endpoints in Atlas.
- IPv6
- A revision to the IP (Internet Protocol) standard with a large address space to support Internet hosts.
- ISODate
- The international date format used by
mongoshto display dates. The format isYYYY-MM-DD HH:MM.SS.millis. - JavaScript
- A scripting language. mongosh, the legacy
mongoshell, and certain server functions use a JavaScript interpreter. See Server-side JavaScript for more information. - journal
- A sequential, binary transaction log used to bring the database into a valid state in the event of a hard shutdown. Journaling writes data first to the journal and then to the core data files. MongoDB enables journaling by default for 64-bit builds of MongoDB version 2.0 and newer. Journal files are pre-allocated and exist as files in the data directory. See Journaling.
- JSON
- JavaScript Object Notation. A plain text format for expressing structured data with support in many programming languages. For more information, see http://www.json.org. Certain MongoDB tools render an approximation of MongoDB BSON documents in JSON format. See MongoDB Extended JSON (v2).
- JSON document
- A JSON document is a collection of fields and values in a structured format. For sample JSON documents, see http://json.org/example.html.
- JSON pointer
- A string prefixed with a
/character that specifies a particular field value in a JSON document. - JSONP
- JSON with padding. Refers to a method of injecting JSON into applications. Presents potential security concerns.
- jumbo chunk
- A chunk that grows beyond the specified chunk size and cannot split into smaller chunks. For more details, see Indivisible/Jumbo Chunks.
- K-nearest neighbor search
- Given a set of points P with a defined similarity function S, for a query point q, finds the set of k points in P with the best values of S*(*p, q). Vector Search ENN search returns the exact top k points and ANN search returns k points that are similar to q, but not necessarily the k most similar to q.
- key material
- The random string of bits used by an encryption algorithm to encrypt and decrypt data.
- key vault collection
- A MongoDB collection that stores the encrypted Data Encryption Keys as BSON documents.
- LDAP
- Cross-platform protocol used to authenticate users and authorize them to access data on a cluster. You can use MongoDB Atlas to manage user authentication and authorization from all MongoDB clients using your own LDAP server over TLS. A single LDAPS configuration applies to all clusters in an MongoDB Atlas project.
- least privilege
- An authorization policy that grants a user only the access that is essential to that user's work.
- legacy coordinate pairs
- The format used for geospatial data before MongoDB version 2.4. This format stores geospatial data as points on a planar coordinate system (for example,
[ x, y ]). See Geospatial Queries. - LineString
- A LineString is an array of two or more positions. A closed LineString with four or more positions is called a LinearRing, as described in the GeoJSON LineString specification: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7946#section-3.1.4. To use a LineString in MongoDB, see GeoJSON Objects.
- link-token
- String that contains the information necessary to connect from Cloud Manager or Ops Manager to MongoDB Atlas during a live migration from a Cloud Manager or Ops Manager deployment to a cluster in MongoDB Atlas.
- little-endian
A byte order in which the least significant byte (little end) of a multibyte data value is stored at the lowest memory address.
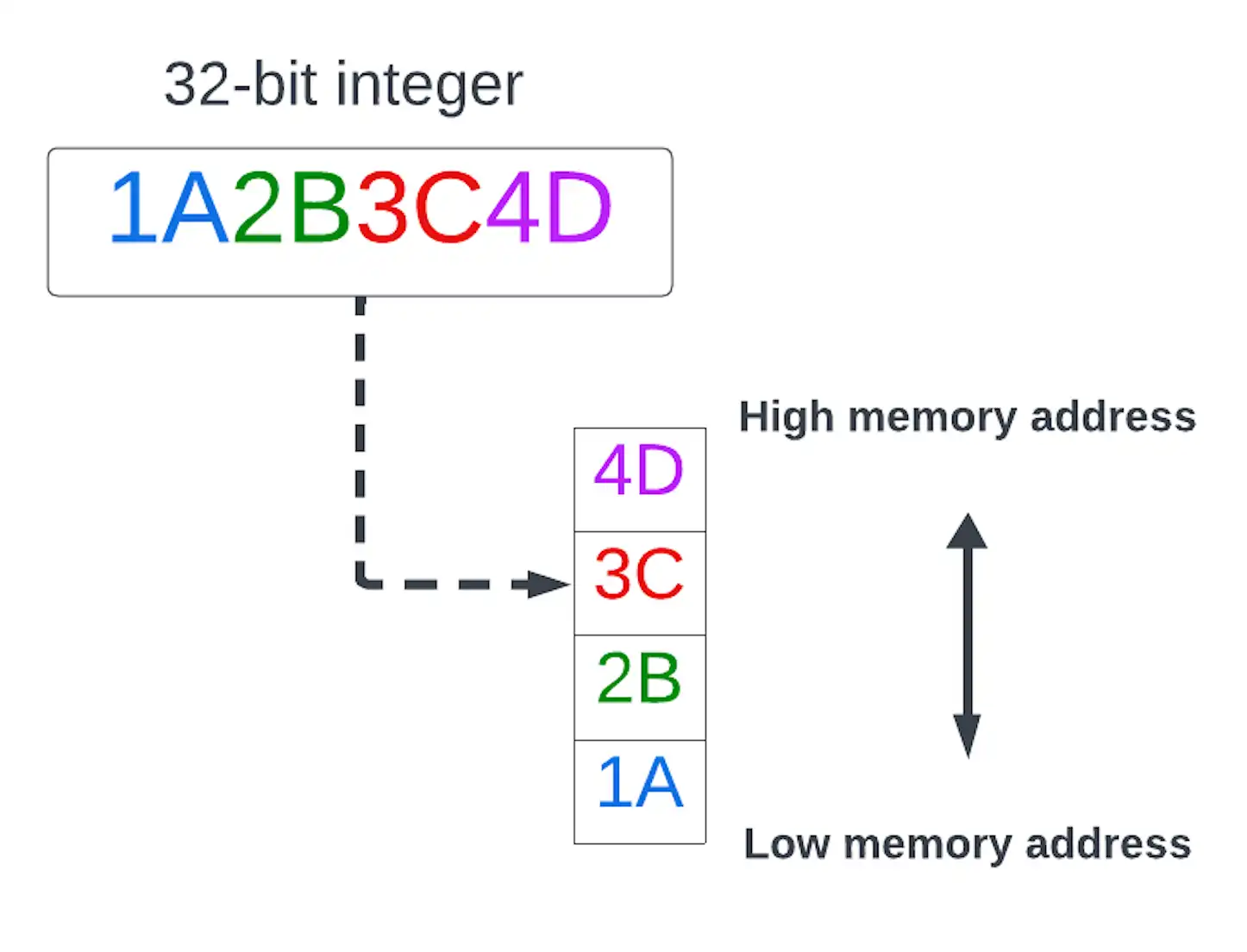 click to enlarge
click to enlarge- live migration
Process to seamlessly move an existing source replica set or sharded cluster to MongoDB Atlas. During the live migration process, MongoDB Atlas keeps the target cluster in sync with the remote source until you cut your applications over to the MongoDB Atlas cluster.
- lock
- MongoDB uses locks to ensure that concurrency does not affect correctness. MongoDB uses read locks, write locks and intent locks. For more information, see What type of locking does MongoDB use?.
- log files
- Contain server events, such as incoming connections, commands run, and issues encountered. For more details, see Log Messages.
- LVM
- Logical volume manager. LVM is a program that abstracts disk images from physical devices and provides a number of raw disk manipulation and snapshot capabilities useful for system management. For information on LVM and MongoDB, see Back Up and Restore Using LVM on Linux.
- maintenance window
Day and time of the week when MongoDB Atlas should start weekly maintenance on your cluster. You can set your maintenance window in your Project Settings.
Important
Maintenance Window Considerations
Urgent Maintenance Activities Urgent maintenance activities such as security patches cannot wait for your chosen window. MongoDB Atlas will start those maintenance activities when needed.
Ongoing Maintenance Operations Once maintenance is scheduled for your cluster, you cannot change your maintenance window until the current maintenance efforts have completed.
Maintenance Requires Replica Set Elections MongoDB Atlas performs maintenance the same way as the maintenance procedure described in the MongoDB Manual. This procedure requires at least one replica set election during the maintenance window per replica set.
Maintenance Starts As Close to the Hour As Possible Maintenance always begins as close to the scheduled hour as possible, but in-progress cluster updates or unexpected system issues could delay the start time.
- map-reduce
- An aggregation process that has a "map" phase that selects the data and a "reduce" phase that transforms the data. In MongoDB, you can run arbitrary aggregations over data using map-reduce. For the map-reduce implementation, see Map-Reduce. For all approaches to aggregation, see Aggregation Operations.
- mapping type
- A structure in programming languages that associate keys with values. Keys may contain embedded pairs of keys and values (for example, dictionaries, hashes, maps, and associative arrays). The properties of these structures depend on the language specification and implementation. Typically, the order of keys in mapping types is arbitrary and not guaranteed.
- md5
- A hashing algorithm that calculates a checksum for the supplied data. The algorithm returns a unique value to identify the data. MongoDB uses md5 to identify chunks of data for GridFS. See filemd5 (database command).
- mean
- Average of a set of numbers.
- median
- In a dataset, the median is the percentile value where 50% of the data falls at or below that value.
- member
- An individual mongod process. A replica set has multiple members. A member is also known as a node.
- metadata collection
- In Queryable Encryption, the internal collections MongoDB uses to enable querying on encrypted fields. See Metadata Collections.
- MIME
- Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions. A standard set of type and encoding definitions used to declare the encoding and type of data in multiple data storage, transmission, and email contexts. The
mongofilestool provides an option to specify a MIME type to describe a file inserted into GridFS storage. - mode
- Number that occurs most frequently in a set of numbers.
- mongo
The legacy MongoDB shell. The
mongoprocess starts the legacy shell as a daemon connected to either amongodormongosinstance. The shell has a JavaScript interface.Starting in MongoDB v5.0,
mongois deprecated and mongosh replacesmongoas the client shell. See mongosh.- mongod
- The MongoDB database server. The
mongodprocess starts the MongoDB server as a daemon. The MongoDB server manages data requests and background operations. Seemongod. - MongoDB Charts
Visualization tool for your MongoDB Atlas data. You can launch MongoDB Charts from your MongoDB Atlas cluster and view your data with the Charts application to begin visualizing your data.
Tip
- MongoDB Search
Fine-grained text indexing enabling advanced text search on your data without any additional required management. MongoDB Search provides options for several kinds of text analyzers, score-based results ranking, and a rich query language.
- mongos
- The MongoDB sharded cluster query router. The
mongosprocess starts the MongoDB router as a daemon. The MongoDB router acts as an interface between an application and a MongoDB sharded cluster and handles all routing and load balancing across the cluster. SeemongosInstances. - mongosh
MongoDB Shell. mongosh provides a shell interface to either a
mongodor amongosinstance.Starting in MongoDB v5.0, mongosh replaces
mongoas the preferred shell.- multi-region cluster
MongoDB Atlas cluster spanning multiple geographic regions. Multi-region clusters can increase availability and improve performance by routing application queries to the most appropriate geographic regions.
Multi-region clusters must contain electable nodes.
Multi-region clusters may contain read-only nodes and analytics nodes.
- namespace
- A namespace is a combination of the database name and the name of the collection or index:
<database-name>.<collection-or-index-name>. All documents belong to a namespace. See Namespaces. - Namespace Insights
MongoDB Atlas tool that monitors collection-level query latency. You can view query latency metrics and statistics for certain hosts and operation types. Manage pinned namespaces and choose up to five namespaces to show in the corresponding query latency charts.
- natural order
The order
recordIdsare created and stored in the WiredTiger index. The default sort order for a collection scan run on a single instance is natural order.In replica sets, natural order is not guaranteed to be consistent and can differ between members.
In sharded collections, natural order is not defined. However, using
$naturalstill forces each shard to perform a collection scan.For details, see Return in Natural Order.
- network partition
A network failure that separates a distributed system into partitions such that nodes in one partition cannot communicate with the nodes in the other partition.
Sometimes, partitions are partial or asymmetric. An example partial partition is the a division of the nodes of a network into three sets, where members of the first set cannot communicate with members of the second set, and the reverse, but all nodes can communicate with members of the third set.
In an asymmetric partition, communication may be possible only when it originates with certain nodes. For example, nodes on one side of the partition can communicate with the other side only if they originate the communications channel.
- network peering connection
Process by which two Internet networks connect and exchange traffic. You can directly peer your VPC with the MongoDB Atlas VPC created for your MongoDB clusters. Using network peering, your application servers can directly connect to MongoDB Atlas while remaining isolated from public networks.
- node
- An individual mongod process. A replica set has multiple nodes. A node is also known as a member.
- noop
- No Operation (noop), is an I/O operation scheduler that allocates I/O bandwidth for incoming processes based on a first in, first out queue.
- normalized string
- The Unicode Normalized Form of a string applies Unicode code points in a standardized manner. Two strings may appear identical to a user, but have differences such as the order of combining marks. Normalizing the strings ensures they have the same binary representation.
- NVMe
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a protocol for accessing high-speed storage media.
- NVMe storage
Available for M40+ clusters hosted on AWS
For applications hosted on AWS which require low-latency and high-throughput IO, you can use the NVMe cluster class. The NVMe cluster class leverages a unique data protocol to greatly improve data access speeds.
NVMe clusters use a hidden secondary node consisting of a provisioned volume with high throughput and IOPS to facilitate backup.
- object identifier
- See ObjectId.
- ObjectId
- A 12-byte BSON type that is unique within a collection. The ObjectId is generated using the timestamp, computer ID, process ID, and a local process incremental counter. MongoDB uses ObjectId values as the default values for _id fields.
- operation log
- See oplog.
- operation metadata
- Information about the execution of processes rather than their content, such as the number and time of insert, update, and delete operations.
- operation rejection filter
- A rejected query shape. For more details, see Block Slow Queries with Operation Rejection Filters.
- operation time
- See optime.
- operational node
- Any electable node or a read-only node in your MongoDB Atlas cluster.
- operator
- A keyword beginning with
$used to express MQL components such as query predicates, expressions, and aggregation stages. For example,$gtis the MQL "greater than" operator. For available operators, see MongoDB Query Language Reference. - oplog
- A capped collection that stores an ordered history of logical writes to a MongoDB database. The oplog is the basic mechanism enabling replication in MongoDB. See Replica Set Oplog.
- oplog buffer collection
A temporary collection created during resharding operations that stores oplog entries from a donor shard.
Oplog buffer collections ensure that recipient shards can access oplog entries when they get deleted from the donor shard. Oplog buffer collections are removed when resharding is complete.
- oplog hole
- A temporary gap in the oplog because the oplog writes aren't in sequence. Replica set primaries apply oplog entries in parallel as a batch operation. As a result, temporary gaps in the oplog can occur from entries that aren't yet written from a batch.
- oplog window
- oplog entries are time-stamped. The oplog window is the time difference between the newest and the oldest timestamps in the
oplog. If a secondary node loses connection with the primary, it can only use replication to sync up again if the connection is restored within the oplog window. - optime
A reference to a position in the replication oplog. The optime value is a document that contains:
- ordered query plan
- A query plan that returns results in the order consistent with the
sort()order. See Query Plans. - organization
Logical grouping of MongoDB Atlas projects. You can leverage an organization to manage billing, users, and security settings for the projects it contains.
- Billing happens at the organization level while preserving visibility into usage in each project.
- You can view all projects within an organization.
- You can use teams to bulk assign organization users to projects within the organization.
Tip
- organization ID
- Unique 24-digit hexadecimal string used to identify your MongoDB Atlas organization. The Return All Organizations endpoint returns the ID of all organizations that the authenticated user executing the API call can access.
- orphaned cursor
- A cursor that is not correctly closed or iterated over in your application code. Orphaned cursors can cause performance issues in your MongoDB deployment.
- orphaned document
In a sharded cluster, orphaned documents are those documents on a shard that also exist in chunks on other shards. This is caused by a failed migration or an incomplete migration cleanup because of an atypical shutdown.
Orphaned documents are cleaned up automatically after a chunk migration completes. You no longer need to run
cleanupOrphanedto delete orphaned documents.- passive member
- A member of a replica set that cannot become primary because its
members[n].priorityis0. See Priority 0 Replica Set Members. - per-CPU cache
- A type of cache that locally stores memory for a specific CPU core. Per-CPU caches are used by the new version of TCMalloc, which is introduced in MongoDB 8.0.
- per-thread cache
- A type of cache that locally stores memory for each application thread. Per-thread caches are used by the legacy version of TCMalloc, which is used in MongoDB 7.0 and earlier.
- percentile
- In a dataset, a percentile is a value where that percentage of the data is at or below the specified value. For details, see Calculation Considerations.
- Performance Advisor
MongoDB Atlas tool that monitors slow queries executed on your cluster and suggests indexes to improve query performance. Each index that the Performance Advisor suggests include an impact score indicating the potential performance improvement that index would bring.
- PID
- A process identifier. UNIX-like systems assign a unique-integer PID to each running process. You can use a PID to inspect a running process and send signals to it. See
/procFile System. - pipe
- A communication channel in UNIX-like systems allowing independent processes to send and receive data. In the UNIX shell, piped operations allow users to direct the output of one command into the input of another.
- pipeline
- A series of operations in an aggregation. See Aggregation Pipeline.
- plan cache query shape
A combination of query predicate, sort, projection, and collation. The plan cache query shape allows MongoDB to identify equivalent queries and analyze their performance.
For the query predicate, only the predicate structure and field names are used. The values in the query predicate aren't used. For example, a query predicate
{ type: 'food' }is equivalent to{ type: 'drink' }.To identify slow queries with the same plan cache query shape, each plan cache query shape has a hexadecimal
planCacheShapeHashvalue. For more information, see planCacheShapeHash and planCacheKey.Starting in MongoDB 8.0, the existing
queryHashfield is duplicated in a new field namedplanCacheShapeHash. If you're using an earlier MongoDB version, you'll only see thequeryHashfield. Future MongoDB versions will remove the deprecatedqueryHashfield, and you'll need to use theplanCacheShapeHashfield instead.- point
- A single coordinate pair as described in the GeoJSON Point specification: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7946#section-3.1.2. To use a Point in MongoDB, see GeoJSON Objects.
- polygon
An array of LinearRing coordinate arrays, as described in the GeoJSON Polygon specification: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7946#section-3.1.6. For Polygons with multiple rings, the first must be the exterior ring and any others must be interior rings or holes.
MongoDB does not permit the exterior ring to self-intersect. Interior rings must be fully contained within the outer loop and cannot intersect or overlap with each other. See GeoJSON Objects.
- post-image document
- A document after it was inserted, replaced, or updated. See Change Streams with Document Pre- and Post-Images.
- powerOf2Sizes
- A setting for each collection that allocates space for each document to maximize storage reuse and reduce fragmentation.
powerOf2Sizesis the default for TTL Collections. To change collection settings, seecollMod. - pre-image document
- A document before it was replaced, updated, or deleted. See Change Streams with Document Pre- and Post-Images.
- pre-splitting
- An operation performed before inserting data that divides the range of possible shard key values into chunks to facilitate easy insertion and high write throughput. In some cases pre-splitting expedites the initial distribution of documents in sharded cluster by manually dividing the collection rather than waiting for the MongoDB balancer to do so. See Create Ranges in a Sharded Cluster.
- prefix compression
- Reduces memory and disk consumption by storing any identical index key prefixes only once, per page of memory. See: Compression for more about WiredTiger's compression behavior.
- primary
- In a replica set, the primary is the member that receives all write operations. See Primary.
- primary key
- A record's unique immutable identifier. In RDBMS software, the primary key is typically an integer stored in each row's
idfield. In MongoDB, the _id field stores a document's primary key, which is typically a BSON ObjectId. - primary shard
- Each database in a sharded cluster has a primary shard. It is the default shard for all unsharded collections in the database. See Primary Shard.
- priority
- A configurable value that helps determine which members in a replica set are most likely to become primary. See
members[n].priority. - privilege
- A combination of specified resource and actions permitted on the resource. See privilege.
- project
Logical grouping of clusters. You can have multiple clusters within a single project and multiple projects within a single organization.
Note
Project is synonymous with group.
- project ID
Unique 24-digit hexadecimal string used to identify your MongoDB Atlas project. The Get All Projects API endpoint returns the ID of all projects that the authenticated user executing the API call can access.
Note
Project ID is synonymous with group ID.
- projection
- A document supplied to a query that specifies the fields MongoDB returns in the result set. For more information about projections, see Project Fields to Return from Query.
- quantization
- Method of compressing the value of individual dimensions in a vector into a smaller range to reduce resource consumption and improve speed. Vector Search supports indexing and querying quantized vectors.
- query
- A read request. MongoDB uses a JSON form of query language that includes query operators with names that begin with a
$character. Inmongosh, you can run queries using thedb.collection.find()anddb.collection.findOne()methods. See Query Documents. - query framework
- A combination of the query optimizer and query execution engine that processes an operation.
- query operator
- A keyword beginning with
$in a query. For example,$gtis the "greater than" operator. For a list of query operators, see query operators. - query optimizer
- A process that generates query plans. For each query, the optimizer generates a plan that matches the query to the index that returns the results as efficiently as possible. The optimizer reuses the query plan each time the query runs. If a collection changes significantly, the optimizer creates a new query plan. See Query Plans.
- query plan
- Most efficient execution plan chosen by the query planner. For more details, see Query Plans.
- query predicate
An expression that returns a boolean indicating whether a document matches the specified query. For example,
{ name: { $eq: "Alice" } }, which returns documents that have a field"name"whose value is the string"Alice".Query predicates can contain child expressions and operators for more complex matching. To see available query operators, see Query Predicates.
- Query Profiler
- MongoDB Atlas tool that diagnoses and monitors performance issues in your cluster. The Query Profiler can expose long-running queries and their performance statistics. You can filter the data returned by the Query Profiler to hone in on specific namespaces and operation types.
- query shape
- A query shape is a set of specifications that group similar queries. For details, see Query Shapes.
- range
- A contiguous range of shard key values within a chunk. Data ranges include the lower boundary and exclude the upper boundary. MongoDB migrates data when a shard contains too much data of a collection relative to other shards. See Data Partitioning with Chunks and Sharded Cluster Balancer.
- RDBMS
- Relational Database Management System. A database management system based on the relational model, typically using SQL as the query language.
- read concern
- Specifies a level of isolation for read operations. For example, you can use read concern to only read data that has propagated to a majority of nodes in a replica set. See Read Concern.
- read lock
- A shared lock on a resource such as a collection or database that, while held, allows concurrent readers but no writers. See What type of locking does MongoDB use?.
- read preference
- A setting that determines how clients direct read operations. Read preference affects all replica sets, including shard replica sets. By default, MongoDB directs reads to primaries. However, you may also direct reads to secondaries for eventually consistent reads. See Read Preference.
- read-only node
- Replica set in a dedicated geographic region that supplements your electable node regions. You can use read-only nodes to localize data where it is most frequently read to improve performance.
- Real-Time Performance Panel
MongoDB Atlas monitoring service that displays current network traffic, database operations on your clusters, and hardware statistics about your host machines. Use the RTPP to visually evaluate query execution times, monitor network activity, and discover potential replication lag on secondary members of replica sets.
- recall
- Measures the fraction of true nearest neighbors that were returned by an ANN search. This measure reflects how close the algorithm approximates the results of ENN search. The notation Recall@k refers to the measurement of how many of the true nearest neighbors were present in the top k results returned by Vector Search.
- recovering
- A replica set member status indicating that a member is not ready to begin activities of a secondary or primary. Recovering members are unavailable for reads.
- relative system CPU utilization
The CPU utilization relative to the amount of baseline CPU assigned to a cloud instance. You can calculate relative system CPU utilization by dividing the absolute system CPU utilization by the amount of baseline CPU assigned to a cloud instance.
MongoDB caps relative system CPU utilization at 100%. When a cloud provider throttles CPU utilization for a cloud instance, or bursts CPU utilization for an instance above the baseline amount of CPU available to that instance, the relative system CPU value is 100%.
See also absolute system CPU utilization, and burstable instances.
- replica set
- Group of MongoDB servers that maintain the same data set. Replica sets provide redundancy, high availability, and are the basis for all production deployments.
- replication
- A feature allowing multiple database servers to share the same data. Replication ensures data redundancy and enables load balancing. See Replication.
- replication lag
- The time period between the last operation in the primary's oplog and the last operation applied to a particular secondary. You typically want replication lag as short as possible. See Replication Lag.
- resident memory
- The subset of an application's memory currently stored in physical RAM. Resident memory is a subset of virtual memory, which includes memory mapped to physical RAM and to storage.
- resource
- A database, collection, set of collections, or cluster. A privilege permits actions on a specified resource. See resource.
- role
- A set of privileges that permit actions on specified resources. Roles assigned to a user determine the user's access to resources and operations. See Security.
- rollback
- A process that reverts write operations to ensure the consistency of all replica set members. See Rollbacks During Replica Set Failover.
- rolling restart
- Process that restarts all nodes in the cluster in sequence. To maintain cluster availability, MongoDB Atlas restarts one node at a time starting with a secondary node. MongoDB Atlas always maintains a primary node until the rolling restart completes.
- scalar quantization
- Scalar quantization involves selecting the minimum and maximum values across all indexed vectors within a segment for each dimension, and producing equally sized bins between them. The mappings for each of these dimensions to the bins yields the new quantized values. Vector Search supports automatic scalar quantization for your float32 vectors, and ingestion and indexing of your scalar quantized vectors from embedding providers.
- secondary
- A replica set member that replicates the contents of the master database. Secondary members may run read requests, but only the primary members can run write operations. See Secondaries.
- secondary index
- A database index that improves query performance by minimizing the amount of work that the query engine must perform to run a query. See Indexes.
- secondary member
- See secondary. Also known as a secondary node.
- seed list
- A seed list is used by drivers and clients (like
mongosh) for initial discovery of the replica set configuration. Seed lists can be provided as a list ofhost:portpairs (see Standard Connection String Format or through DNS entries.) For more information, see SRV Connection Format. - self-managed
- A MongoDB instance that is set up and maintained by an individual or organization, and not an external management or third-party services (such as MongoDB Atlas).
- semantic search
- Search for values that have a similar meaning to query. Semantic search captures the natural relationship between words or phrases even when there is no lexical overlap. Semantic search and vector search are often used interchangeably. Vector Search supports semantic search on vector data stored in MongoDB Atlas clusters.
- set name
- The arbitrary name given to a replica set. All members of a replica set must have the same name specified with the
replSetNamesetting or the--replSetoption. - shard
- A single
mongodinstance or replica set that stores part of a sharded cluster's total data set. Typically, in a production deployment, ensure all shards are part of replica sets. See Shards. - shard key
- The field MongoDB uses to distribute documents among members of a sharded cluster. See Shard Keys.
- sharded cluster
- The set of nodes comprising a sharded MongoDB deployment. A sharded cluster consists of config servers, shards, and one or more
mongosrouting processes. See Sharded Cluster Components. - sharding
- A database architecture that partitions data by key ranges and distributes the data among two or more database instances. Sharding enables horizontal scaling. See Sharding.
- shared cluster
Cluster category containing
M0(free tier) tier clusters. Shared clusters are generally used for development and small production workloads.- shell helper
- A method in
mongoshthat has a concise syntax for a database command. Shell helpers improve the interactive experience. SeemongoshMethods. - similarity function
- Measures the similarity between two vectors. Vector Search supports
euclidean,cosine, anddotProductsimilarity functions. - single-master replication
- A replication topology where only a single database instance accepts writes. Single-master replication ensures consistency and is the replication topology used by MongoDB. See Replica Set Primary.
- snappy
- A compression/decompression library to balance efficient computation requirements with reasonable compression rates. Snappy is the default compression library for MongoDB's use of WiredTiger. See Snappy and the WiredTiger compression documentation for more information.
- snapshot
- A snapshot is a copy of the data in a
mongodinstance at a specific point in time. You can retrieve snapshot metadata for the whole cluster or replica set, or for a single config server in a cluster. - softIRQ
- The CPU utilization metric that reflects a portion of CPU that a cloud instance currently uses to process software interrupt requests. On some cloud providers, this metric is useful for tracking CPU utilization on burstable instances.
- sort key
- The value compared against when sorting fields. To learn how MongoDB determines the sort key for non-numeric fields, see Comparison/Sort Order.
- split
- The division between chunks in a sharded cluster. See Data Partitioning with Chunks.
- SQL
- Structured Query Language (SQL) is used for interaction with relational databases.
- SSD
- Solid State Disk. High-performance storage that uses solid state electronics for persistence instead of rotating platters and movable read/write heads used by mechanical hard drives.
- stale read
- A stale read refers to when a transaction reads old (stale) data that has been modified by another transaction but not yet committed to the database.
- standalone
An instance of
mongodthat runs as a single server and not as part of a replica set. To convert a standalone instance to a replica set, see Convert a Standalone Self-Managed mongod to a Replica Set.Note
A standalone instance is not a replica set with only one member.
- stash collection
A temporary collection created on the recipient shard for each donor shard during resharding operations.
Stash collections temporarily hold documents that cannot be immediately inserted due to operation conflicts. For example, if a document's shard key has been updated, it now belongs to a different shard, and the order of operations applied to this document can be ambiguous. The recipient stores these documents in a stash collection until it can apply operations in the correct order.
- step down
The primary member of the replica set removes itself as primary and becomes a secondary member.
- If a replica set loses contact with the primary, the secondaries elect a new primary. When the old primary learns of the election, it steps down and rejoins the replica set as a secondary.
- If the user runs the
replSetStepDowncommand, the primary steps down, forcing the replica set to elect a new primary.
- storage engine
- The part of a database that is responsible for managing how data is stored and accessed, both in memory and on disk. Different storage engines perform better for specific workloads. See Storage Engines for Self-Managed Deployments for specific details on the built-in storage engines in MongoDB.
- storage order
- See natural order.
- strict consistency
- A property of a distributed system requiring that all members contain the latest changes to the system. In a database system, this means that any system that can provide data must contain the latest writes.
- Subject Alternative Name
- Subject Alternative Name (SAN) is an extension of the X.509 certificate which allows an array of values such as IP addresses and domain names that specify the resources a single security certificate may secure.
- sync
- The replica set operation where members replicate data from the primary. Sync first occurs when MongoDB creates or restores a member, which is called initial sync. Sync then occurs continually to keep the member updated with changes to the replica set's data. See Replica Set Data Synchronization.
- syslog
- On UNIX-like systems, a logging process that provides a uniform standard for servers and processes to submit logging information. MongoDB provides an option to send output to the host's syslog system. See
syslogFacility. - tag
A label applied to a replica set member and used by clients to issue data-center-aware operations. For more information on using tags with replica sets, see Read Preference Tag Set Lists.
- tag set
- A document containing zero or more tags.
- tailable cursor
- For a capped collection, a tailable cursor is a cursor that remains open after the client exhausts the results in the initial cursor. As clients insert new documents into the capped collection, the tailable cursor continues to retrieve documents.
- team
- Group of Atlas users in the same organization. You can use teams to grant access to the same group of Atlas users across multiple projects. All users in the team share the same project access.
- term
- For the members of a replica set, a monotonically increasing number that corresponds to an election attempt.
- time series collection
- A collection that efficiently stores sequences of measurements over a period of time. See Time Series.
- topology
The state of a deployment of MongoDB instances. Includes:
- Type of deployment (standalone, replica set, or sharded cluster).
- Availability of servers.
- Role of each server (primary, secondary, config server, or
mongos).
- transaction
- Group of read or write operations. For details, see Transactions.
- transaction coordinator
- A component of MongoDB that manages transactions in a replica set or a sharded cluster. It coordinates the execution and completion of multi-document transactions across nodes and allows a complex operation to be treated as an atomic operation.
- TSV
- A text-based data format consisting of tab-separated values. This format is commonly used to exchange data between relational databases because the format is suited to tabular data. You can import TSV files using
mongoimport. - TTL
- Time-to-live (TTL) is an expiration time or period for a given piece of information to remain in a cache or other temporary storage before the system deletes it or ages it out. MongoDB has a TTL collection feature. See Expire Data from Collections by Setting TTL.
- unbounded array
- An array that consistently grows larger over time. If a document field value is an unbounded array, the array may negatively impact performance. In general, design your schema to avoid unbounded arrays.
- unique index
- An index that enforces uniqueness for a particular field in a single collection. See Unique Indexes.
- unix epoch
- January 1st, 1970 at 00:00:00 UTC. Commonly used in expressing time, where the number of seconds or milliseconds since this point is counted.
- unordered query plan
- A query plan that returns results in an order inconsistent with the
sort()order. See Query Plans. - upsert
An option for update operations. For example:
db.collection.updateOne(),db.collection.findAndModify(). If upsert istrue, the update operation either:- updates the document(s) matched by the query.
- or if no documents match, inserts a new document. The new document has the field values specified in the update operation.
For more information about upserts, see Insert a New Document if No Match Exists (
Upsert).- vector database
- System that stores vector embeddings and associated metadata, and enables nearest neighbor search on the stored vector embeddings. You can use MongoDB Atlas as your vector database and Vector Search to perform vector search on the stored vector embeddings. You can use vector database to implement RAG.
- vector index
- Data structure that efficiently processes nearest neighbor search queries. Vector Search supports creating indexes of type
vectorto index fields for running$vectorSearchqueries. - Vector Search
- Feature that allows you to perform semantic search on vector embeddings by comparing query vectors with indexed vectors to find the closest match.
- vector search
- Method of performing k nearest neighbor search over a set of vectors stored in a vector index. Vector Search supports ANN and ENN search for k nearest neighbors.
- virtual memory
- An application's working memory, typically residing on both disk and in physical RAM.
- WGS84
- The default reference system and geodetic datum that MongoDB uses to calculate geometry over an Earth-like sphere for geospatial queries on GeoJSON objects. See the "EPSG:4326: WGS 84" specification: http://spatialreference.org/ref/epsg/4326/.
- window operator
- Returns values from a span of documents from a collection. See window operators.
- working set
- The data that MongoDB uses most often.
- write concern
- Specifies whether a write operation has succeeded. Write concern allows your application to detect insertion errors or unavailable
mongodinstances. For replica sets, you can configure write concern to confirm replication to a specified number of members. See Write Concern. - write conflict
- A situation where two concurrent operations, at least one of which is a write, try to use a resource that violates the constraints for a storage engine that uses optimistic concurrency control. MongoDB automatically ends and retries one of the conflicting write operations.
- write lock
- An exclusive lock on a resource such as a collection or database. When a process writes to a resource, it takes an exclusive write lock to prevent other processes from writing to or reading from that resource. For more information on locks, see FAQ: Concurrency.
- zlib
- A data compression library that provides higher compression rates at the cost of more CPU, compared to MongoDB's use of snappy. You can configure WiredTiger to use zlib as its compression library. See http://www.zlib.net and the WiredTiger compression documentation for more information.
- zone
- A grouping of documents based on ranges of shard key values for a given sharded collection. Each shard in the sharded cluster can be in one or more zones. In a balanced cluster, MongoDB directs reads and writes for a zone only to those shards inside that zone. See the Zones manual page for more information.
- zstd
- A data compression library that provides higher compression rates and lower CPU usage when compared to zlib.